Doctors anxious about pneumonia-related death cases
Pneumonia contracted outside a hospital caused by a staph bacterium, including a "superbug" strain, may be more common in U.S. children than previously thought.
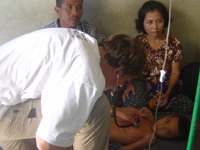
The U.S. Centers for Disease Prevention and Control focused on pneumonia cases caused by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus at three Atlanta-area children's hospitals. Almost half involved a drug-resistant strain known as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, or MRSA, the CDC said.
MRSA is sometimes called a "superbug" because it resists treatments by all but the most powerful antibiotics.
A team led by the CDC's Dr. Alexander Kallen identified 53 children, average age 8-1/2, with pneumonia caused by this bacterium -- more than they expected -- at the three hospitals over seven months during the 2006-2007 flu season. Of these, 22 involved MRSA, the CDC said.
Of six children who died, three had pneumonia involving MRSA, the CDC said. Death occurred an average of 13 days after the onset of symptoms.
Staph bacteria typically are found on the skin or in the nose of about a third of people.
The findings were presented at an infectious diseases conference in Atlanta.
Kallen said in recent years the CDC had heard a large number of reports of rapidly fatal Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia occurring in children.
Kallen said the proportion of the cases involving MRSA was a matter of concern. "It's basically a Staphylococcus aureus bug that's resistant to certain types of antibiotics that are frequently used to treat staph," he said.
While the study involved pediatric pneumonia cases, the same trends may be occurring in adult patients. "We don't have any reason to believe it would be any different," Kallen said.
Pneumonia is a common illness which occurs in all age groups, and is a leading cause of death among the elderly and people who are chronically and terminally ill. Vaccines to prevent certain types of pneumonia are available. The prognosis depends on the type of pneumonia, the appropriate treatment, any complications, and the person's underlying health.
Typical symptoms associated with pneumonia include cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty in breathing. Diagnostic tools include x-rays and examination of the sputum. Treatment depends on the cause of pneumonia; bacterial pneumonia is treated with antibiotics.
Subscribe to Pravda.Ru Telegram channel, Facebook, RSS!





